
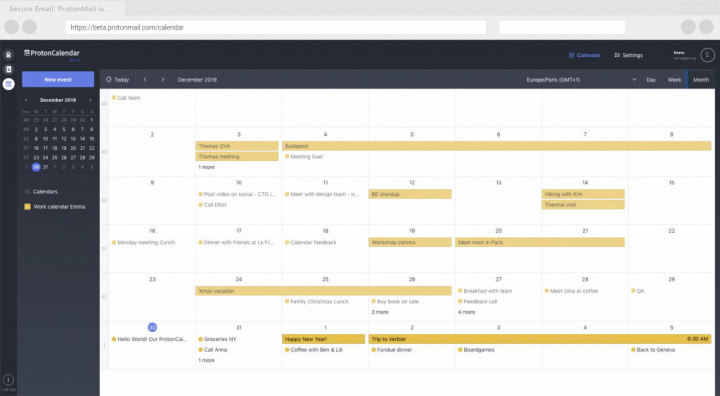
If the endoscopic appearance has atypical characteristics such as irregular surface, redness, erosion, or depression, the polyp should be resected, as these features have been associated with dysplasia and carcinoma. 7 When upper gastrointestinal endoscopy reveals fewer than 20 gastric polyps with the characteristic appearance of FGPs in the gastric body, biopsy is unnecessary. Should she stop using omeprazole?īenign FGPs are typically small (< 1 cm) sessile polyps with a smooth contour found in the body of the stomach.
The patient has taken omeprazole 20 mg daily for many years. Biopsy results showed fundic gland polyps, negative for dysplasia. In addition to short-segment Barrett esophagus, 12 sessile polyps 4 to 6 mm in size were found in the body of her stomach. 14ĬASE 1: FUNDIC GLAND POLYPS, NO DYSPLASIAĪ 65-year-old woman underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy for surveillance of a history of Barrett esophagus without dysplasia. In the rare cases of sporadic FGPs with carcinomas, most are small polyps with a mean size of 5.4 mm, suggesting that even polyp size may not predict malignancy risk.

16 This study may have been limited by its short follow-up period, as reports of cancer with sporadic FGPs do exist. 14, 15 While the risk of dysplasia increases with polyp size in FAP-associated FGPs, a study of 132 large (> 1-cm) sporadic FGPs with a median follow-up of 3.2 years reported a rate of dysplasia of 2.6 cases per 1,000-person years of follow-up and no carcinoma. 14 PPI-associated FGPs have not been linked to an increased risk of malignant transformation compared with the risk in the general population. 6, 13 However, these mutations are not routinely checked in histology.Ĭase reports have described dysplasia in patients with sporadic FGPs who take a PPI, but the true risk of carcinoma in patients with PPI-associated FGPs is unclear. They frequently demonstrate dysplasia, leading to a much higher risk of gastric cancer than PPI-associated FGPs. 11, 12 In contrast, syndromic or FAP-associated FGPs arise through somatic second-hit mutations of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Sporadic or PPI-associated FGPs exhibit activating beta-catenin gene mutations and rarely show dysplasia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
